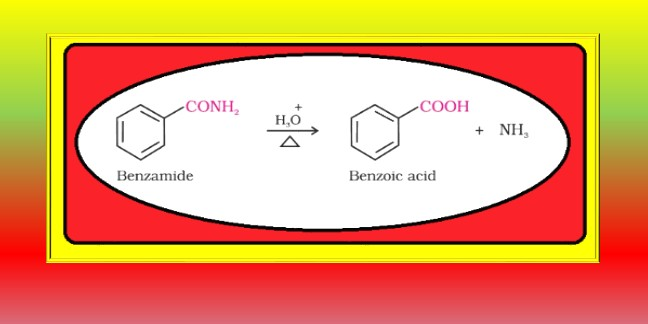
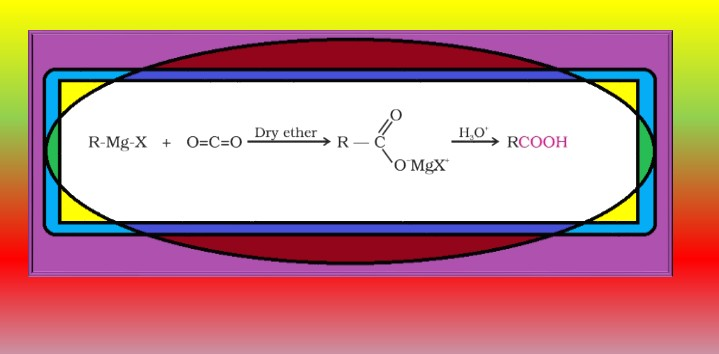
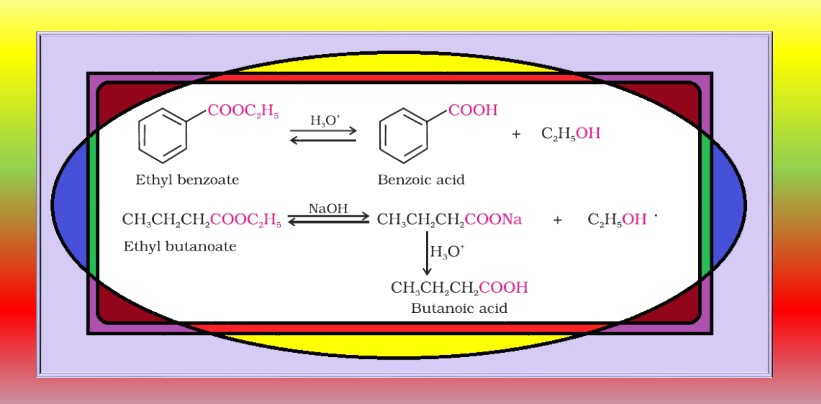
From alkylbenzenes :
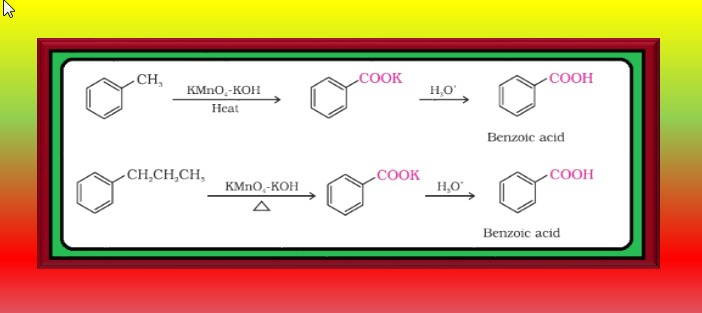
`=>` Aromatic carboxylic acids can be prepared by vigorous oxidation of alkyl benzenes with chromic acid or acidic or alkaline potassium permanganate.
● The entire side chain is oxidised to the carboxyl group irrespective of length of the side chain.
● Primary and secondary alkyl groups are oxidised in this manner while tertiary group is not affected.
● Suitably substituted alkenes are also oxidised to carboxylic acids with these oxidising reagents.
● The entire side chain is oxidised to the carboxyl group irrespective of length of the side chain.
● Primary and secondary alkyl groups are oxidised in this manner while tertiary group is not affected.
● Suitably substituted alkenes are also oxidised to carboxylic acids with these oxidising reagents.